I am thrilled to share a new open-access article in AERA Open that I wrote on the topic of differential tuition policies at public universities. Differential tuition, in which students pay higher charges for fields of study that are more expensive to operate and/or are in high demand among students, have anecdotally become more popular in recent years. Yet the only published research on the effects of differential tuition (a great study that motivated my work) focused on public research universities that adopted differential tuition by the 2007-08 academic year.
I decided to slowly chip away at collecting data on the presence of differential tuition in business, engineering, and nursing programs between the 2003-04 and 2022-23 academic years. It took me more than three months to compile a dataset that you can download here, and then several additional months to do data checks and write the paper (with the help of a new research assistant who debuted during the project and alternated between sleeping and data entry).

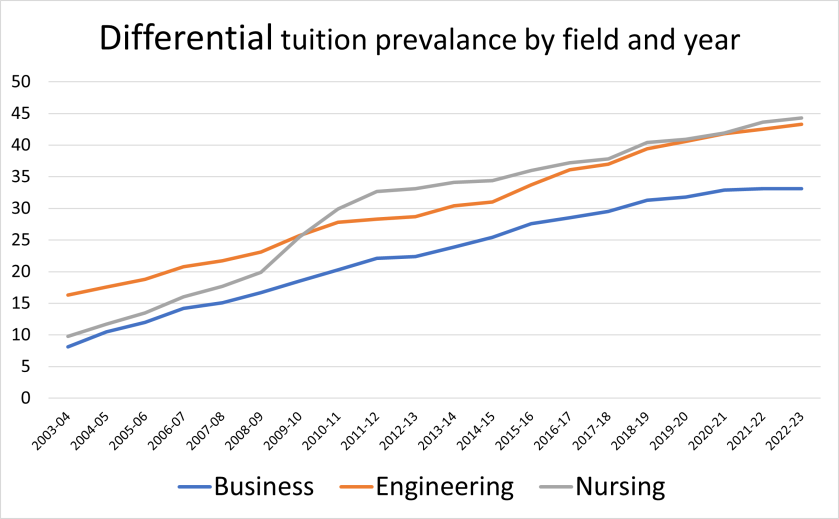
Notably, nearly half of all public universities—and just over half of all research universities—adopted differential tuition by the 2022-23 academic year. While I did not have the resources to collect data on the amount of the differential (funders, reach out if you’re interested in supporting an extension of this work!), differentials ranged from a few dollars per credit hour to several thousand dollars per year.
I then examined whether the adoption of differential tuition increased the number of bachelor’s degrees awarded in business, engineering, or nursing. In general, there were no effects on business or nursing and some modest increases in the number of engineering degrees. However, any benefits of expanded access largely accrued to White students.
Check out the full article and let me know what you think. I am certainly open to extending this work, so any suggestions would be greatly appreciated.
